Subsections of SHARE Data
Data access
Access to SHARE Data
SHARE data are openly accessible for scientific research purposes.
The SHARE data are distributed by the international scientific consortium SHARE-ERIC (Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe – European Research Infrastructure Consortium) to registered users via the SHARE Research Data Center.
Data access is free of charge and adheres to the legislation of the European Union and national data protection laws. Use is governed by publicly available rules.
The data are hosted in cooperation with the following archives:
- CentERdata Archive (Tilburg University, Netherlands)
- GESIS Data Archive (Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences, Cologne, Germany)
Data Files
A complete overview of available data files for all SHARE survey waves, including supplementary data, can be found here:
🔗 SHARE Data Releases
Registration Process
Because the official SHARE-ERIC website is frequently updated, always follow the instructions provided at:
🔗 www.share-eric.eu
Access to SHARE data is free. Registration is required only once – your login credentials remain valid for future data releases.
Summary of Steps:
- All SHARE data are freely accessible at: https://releases.sharedataportal.eu
- Data are hosted at CentERdata and GESIS archives.
- You can download data after completing registration (see below).
- Data are available in STATA and SPSS formats (also usable in R).
- Data documentation is available at the SHARE data portal.
- FAQs are available here
Data from all waves and all special questionnaires (HCAP, COVID-19, accelerometry, life history, national questionnaires and projects) are available for download.
Note: The Czech Republic joined SHARE in Wave 2.
Steps to Register
Step 1: Read the terms of use:
🔗 SHARE Conditions of Use
Step 2: Download and complete this form:
📄 SHARE User Statement (PDF)
Step 3: Submit a pdf scan of the completed and signed form by email to:
📧 E-mail: share-rdc@centerdata.nl
Step 4: If you need any help, please email us at
📧 E-mail: share@cerge-ei.cz
Downloading Data After Registration
Once your registration is processed (usually within a few days), you will receive:
- a personal user ID (login) and an initial password (valid for 72 hours)
Login: https://releases.sharedataportal.eu/users/login
If you forget your credentials or want to reset them, visit:
🔗 SHARE RDC Login Page
SHARE Data Usage Conditions
Please read the official data usage policy:
📄 SHARE Conditions of Use
Citation Requirements and Acknowledgment
According to the
SHARE Citation requirements, every publication using SHARE data must include:
- a proper acknowledgment of the SHARE project
- a reference to the data used
The citation requirements change with each data release, please always use the current citation wording from the official webiste 🔗 https://share-eric.eu/
Main panel
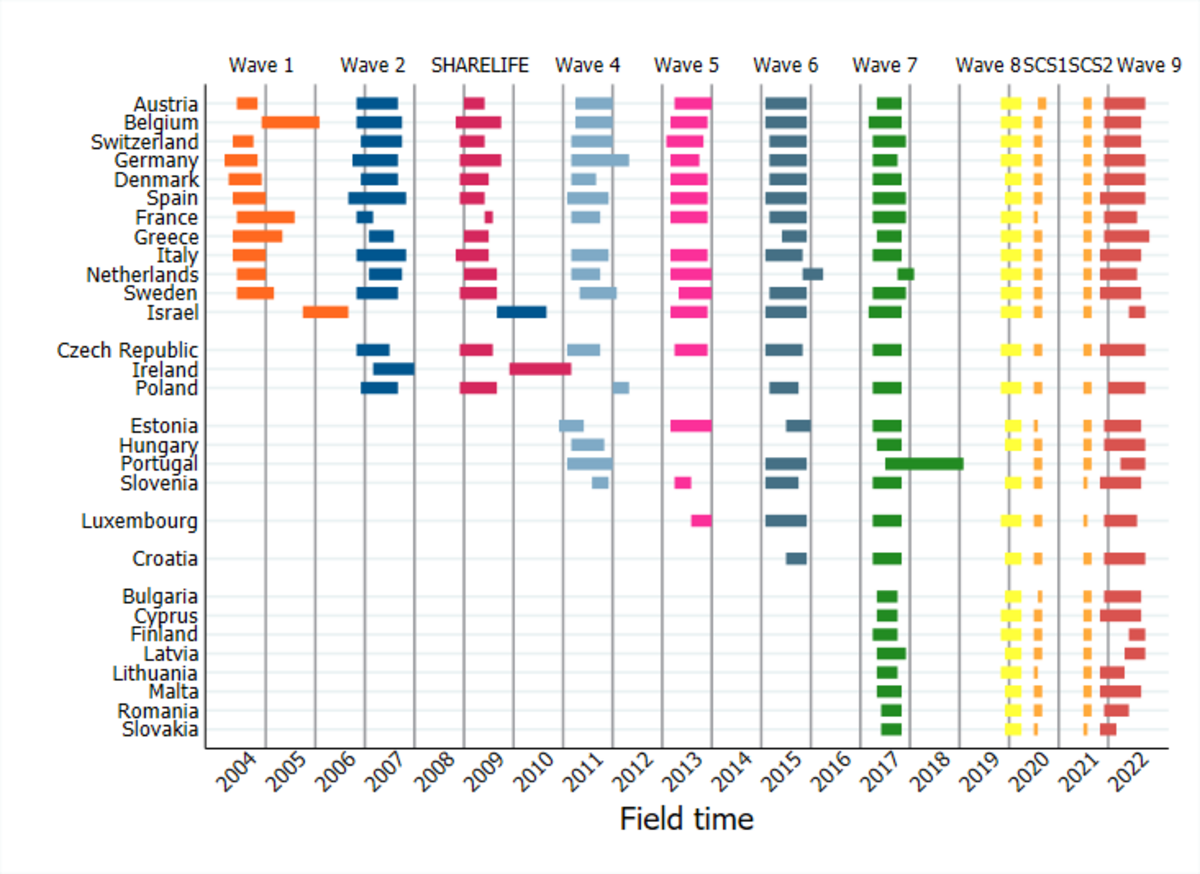
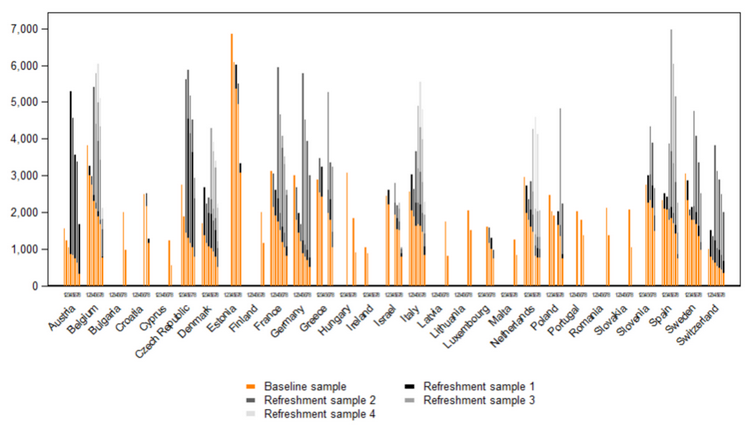
Questionnaire overview
The SHARE main questionnaire consists of around twenty modules. All data are collected by face-to-face, computer-aided personal interviews (CAPI), supplemented by a self-completion paper and pencil questionnaire. Not all respondents have to answer all modules of the questionnaire. The questionnaire modules that rather refer to the household than to the individual are only answered by a designated financial, family, or housing respondent.
The SHARE Questionnaire is the instrument to get valid data. SHARE follows the ex-ante harmonization approach for the design of the questionnaire. It is developed starting from the English version, translated in 39 country-specific languages and adapted to the national institutional framework. The questionnaire consists of a set of core modules and wave specific add-ons.
At the SHARE data portal you can find the generic and language versions of all questionnaires.
Data documentation is cumulatively available in the official Release Guide after each wave and each data release.
SHARE Methodology Volumes
contain detailed information on single survey waves and corresponding methodological background.
Cross Wave Comparison
For questionnaire correspondence across waves the basic rule holds that questions are identically named if the content has not changed.
As changes sometimes have to be conducted due to societal changes (eg. new communication tools) or due to flaws found in the previous waves (e.g. ambiguous understanding of question wording) you will find an overview of the generic versions of the questionnaires in all waves where you can track the deviations between waves.
In order to compare the items across different waves easier, we provide the following two documents:
- the comparison of question texts, response options and interviewer instructions in the main questionnaires of the regular SHARE items
- the comparison of question texts, response options and interviewer instructions in the main questionnaires of the SHARELIFE items of Wave 3 and Wave 7
For a wave N, questions are coded in the following way:
| WN_Question_Text |
Question texts |
| WN_Response_Options |
Response options |
| WN_Interviewer_Instruction |
Interviewer instructions |
| . |
Question has not been asked at all in corresponding wave |
| [none] |
Question has been asked in corresponding wave but no interviewer instruction, response option or in some cases question text (e.g. interviewer observation) was given |
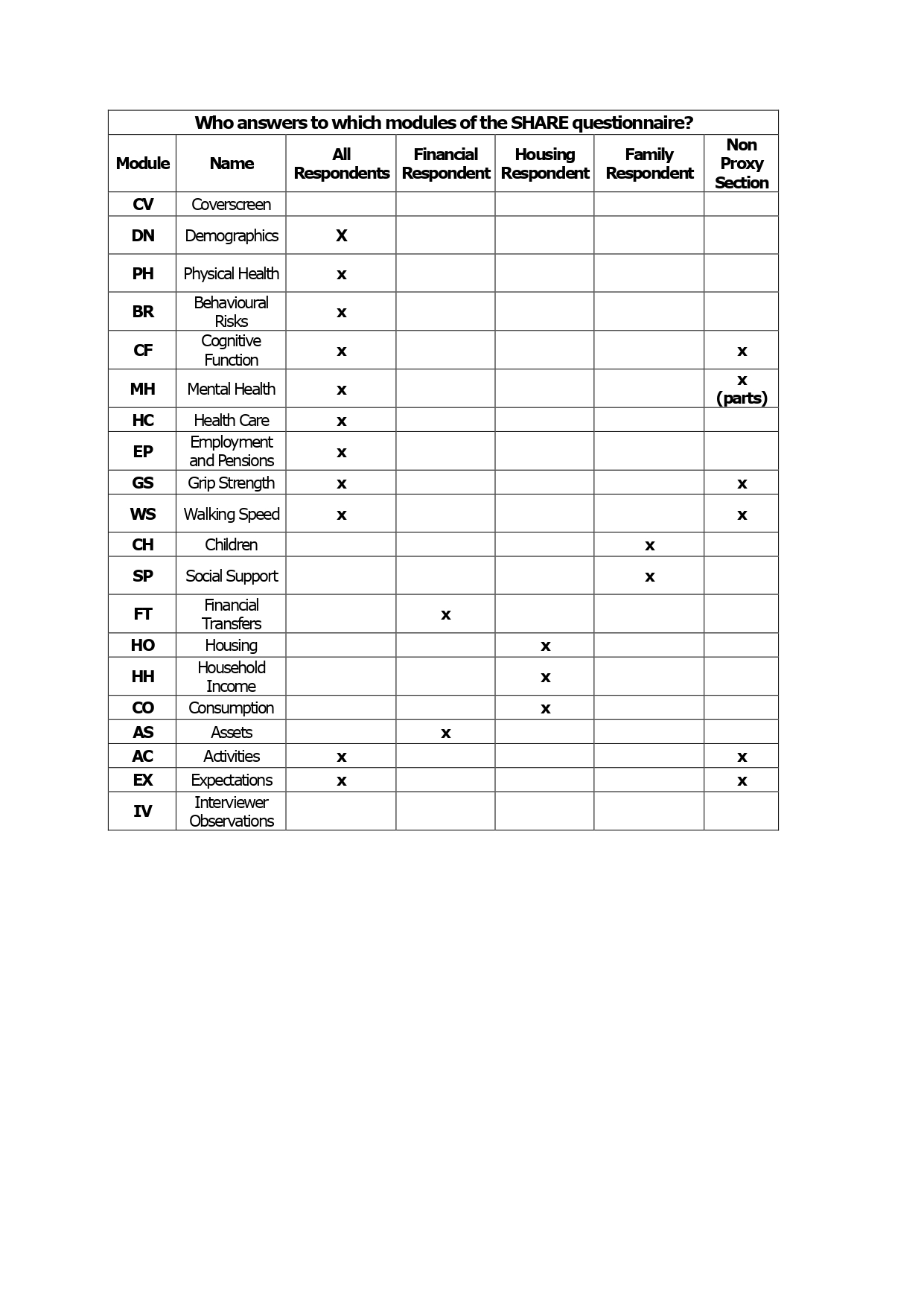
Modules
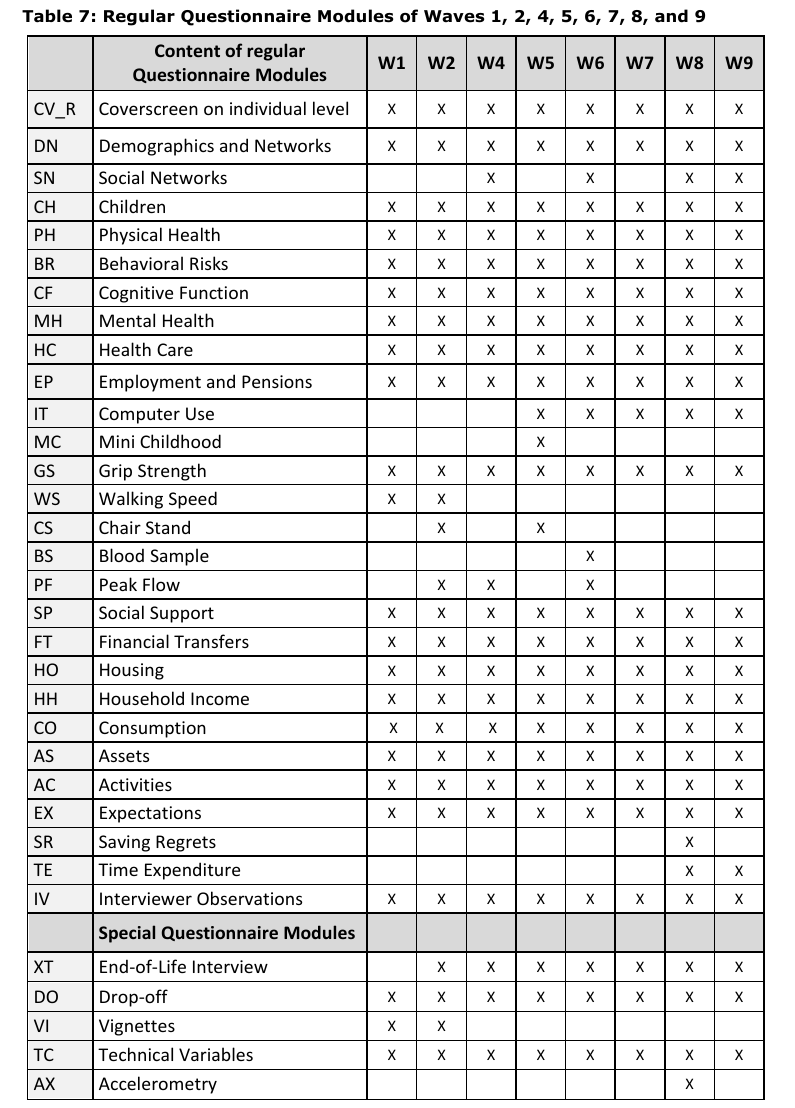
The following table presents the structure of Questionnaire Modules from wave 1 to wave 9.

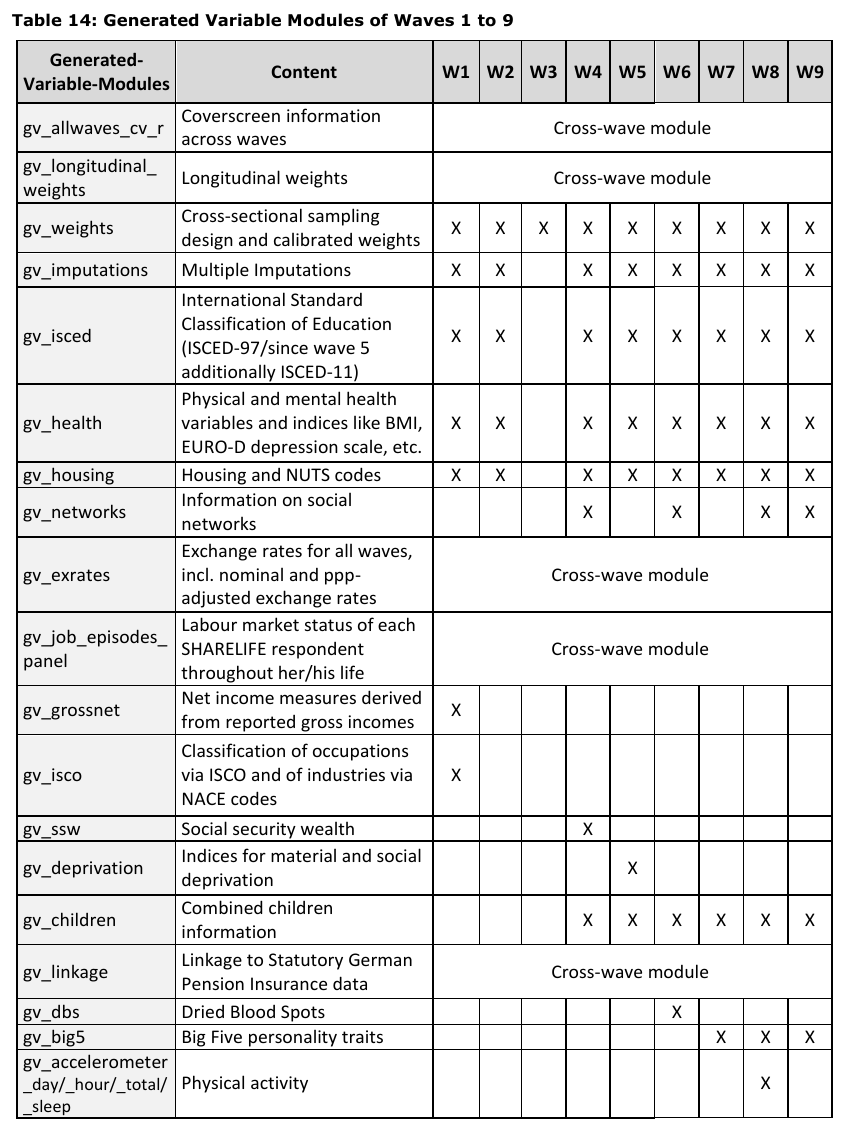
Generated variables
SHARE-ERIC team codes important variables according to their international indexes and standardized variables. These modules are part of each Release. The most important generated variables module is gv_health

Respondent types
Each household consists of the main sampled respondent aged 50+ and his or her partner (who might be younger). Some modules must be answered by each respondent while depending on questionnaire and module content, questions can be answered only by a family, household or financial respondent. Some modules can be answered by a proxy respondent on behalf of a respondent who is unable to answer the questions.

SHARELIFE Life History
SHARELIFE data was collected in wave 3 and wave 7 focusing on respondents’ life histories. Most of the information collected in the regular SHARE waves is about the current life circumstances. As a result, we know little about what happened earlier in the respondents’ lives. SHARELIFE gathers more detailed information on important areas of our respondents’ lives, ranging from partners and children over housing and employment history to detailed questions on health and health care. SHARELIFE data complements the SHARE panel data by providing life history information to enhance our understanding of how early life experiences and events throughout life influence the circumstances of older people. With this variety SHARELIFE constitutes a unique cross-national, interdisciplinary database for research in the fields of sociology, economics, gerontology, and demography.
Collecting accurate retrospective information is a challenge. Respondents may not remember the occurrence or the exact timing of past events perfectly. Therefore, SHARELIFE follows a Life History Calendar (LHC) approach, which has been designed to help respondents in remembering past events more accurately. Using this method, the life events of interest are displayed on a “calendar”, enabling interviewers and respondents to cross-reference certain life-events with others (e.g. “I moved from A to B the year after my first child was born”). Using the life history calendar technique has been shown to improve the accuracy of the retrospective information given by respondents.
Life History Calendar
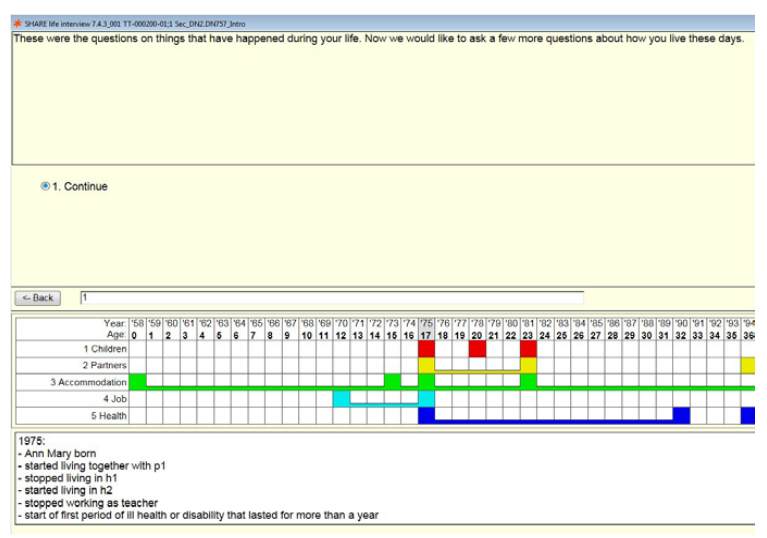

The questioning method used in the SHARELIFE project is based on what is known as a Life History Calendar. The respondent’s life is graphically represented by a grid, which is automatically filled in during the interview.
The idea behind the LHC is to help the respondent remember by first asking about life events that they are likely to remember accurately. The interview usually begins with the names and dates of birth of the respondent’s children (and other information about them), followed by the history of their partners.
Once an event appears in the LHC, the interviewer can refer to it as an aid. For example, if the respondent is unsure of the date of a job change, it may be helpful to ask, “Was it before or after the birth of your second child?”
This principle applies to all other modules and is also flexible: respondents do not have to start with the module on children. If it is easier for them to remember another part of their life, they can start there.
Another aid provided by the LHC is a list of significant events for each year. If the respondent is unsure of the date, the interviewer can help by mentioning or verifying one of these events. For example, if the respondent cannot remember the year their child was born but knows that it was the same year as the occupation of Czechoslovakia in 1968, this information can help the interviewer determine the date.
In Wave 7, the SHARELIFE interview was administered to respondents for whom information on their life histories was still missing. This interview concerned all respondents from countries that joined SHARE after Wave 3 and respondents from “old countries” who were not interviewed in Wave 3, namely, new spouses and respondents from so-called refreshment samples. In total, SHARELIFE data from over 60,000 respondents from 27 countries were collected. This massive data source will be useful for researchers around the world. Respondents whose life histories were already collected in Wave 3 were asked the regular SHARE panel questionnaire (approximately 13,000 respondents).
SHARELIFE – life history calendar modules
The SHARELIFE history calendar records events into a grid, which spans across the respondent’s life course in years, time being the horizontal dimension. Table 2.1 is a tabular itemisation of the SHARE Wave 7 life history calendar, which displays different dimenions of a respondent’s life history:
- Information about the respondent’s offspring
- Information about partners
- Accommodation history
- Employment history
- Health history
Life History Calendar Modules
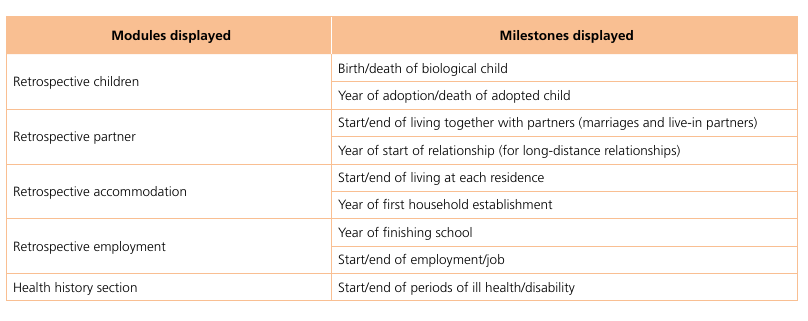

The SHARELIFE interview in Wave 7 spanned various salient domains of a respondent’s life course:
-
The retrospective children questions collected retrospective information on children and deceased children, including information about pregnancies, births, adoptions, characteristics of children and maternity benefits and leave. The information obtained in these areas was contextualised by accompanying follow-up questions about employment and income at the instance of occurrence of certain salient events. For example, there were questions on income sources at the time of motherhood.
-
The retrospective partner questions collected retrospective information on all relationships until the present, including information on living arrangements, cohabitation, marriages, separation, divorces, and death of partners.
-
The retrospective accommodation questions collected information on past and current accommodations, including details of household establishment, residences (country, region), special accommodation events, moves, types of accommodation, cohabitation with parents/children, and ownership.
-
The retrospective employment questions collected data on employment spells, including information about employment status, job characteristics, income, retirement benefits, and employment after retirement. Data are also collected on work quality, job satisfaction, and career breaks due to ill health or disability, disability allowances, insurance and computer skills.
-
The retrospective health questions elicit information about health and healthcare history during both childhood and adulthood, including details about hospital stays, illnesses, injuries, diseases, vaccinations, doctor visits, preventive check-ups, health behaviours, reasons for not going to the doctor, forgone medication, and impact of financial situation on health care.
Information was also collected on childhood circumstances (e.g., childhood health, academic performance, relationship with parents, features of accommodation, books read, companions).
With respect to finances (e.g., insurance, housing, investments), information was collected on financial investments that the respondent may have made during his/her life, including investments in stocks or shares, mutual funds or managed investment accounts, life insurance uptake, business ownership, and overall household income (amount).
Information was also collected on general life events (e.g., periods of hunger, periods of happiness, stress, financial hardship, discrimination at work, respondent and parental experiences of persecution, oppression, and dispossession).
National module
National Module
The SHARE project is fully harmonized with similar studies in the U.S. (HRS), the UK (ELSA), and new initiatives in China, Japan, India, and other countries. As part of the main questionnaire, each country also includes a National Module (originally a self-completion questionnaire, the so-called drop-off), which allows countries to include their own questions. These do not have to be harmonized with other countries and offer a unique opportunity to address locally relevant issues or carry out field experiments that may not be meaningful in other contexts.
Thanks to the support of the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic and in cooperation with the Research Institute for Labor and Social Affairs (RILSA), we included the National Module in waves 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. In all of these collections, we provided external researchers with space in the questionnaire for their questions. For beginning and junior researchers, this is a unique opportunity to collect data on their own topic from a representative sample and, in addition, to combine this data with the main SHARE data, including life history data and other special data collections.
In wave 10, the National Module was used for questions related to the neuroSHARE project.
Invitation to Submit Your Questions for the National Module (in wave 9)
We invite you to participate in the upcoming 9th wave of the SHARE project. The drop-off questionnaire is completed by respondents (or their proxies) after finishing the main CAPI interview. Due to space limitations, questions must be clearly worded, easy to understand (especially considering the age of the respondents), and should not deter participation. Importantly, they must not duplicate questions from the main questionnaire.
Responses must be either numeric or selected from predefined categories—open-ended questions are not allowed. The drop-off will be pretested in autumn 2021 during the main questionnaire pilot. We will analyze responses from the test, remove problematic or non-informative questions, and prepare the final version of the drop-off, which must be approved by the project coordinator.
Data collected from the drop-off will be linked to the main longitudinal SHARE dataset, allowing researchers to relate responses to the respondents’ life histories and other data.
If you are interested in including your own questions in the SHARE drop-off, please contact us at the email addresses below. Before submitting your proposal, we encourage you to review questionnaires from previous waves (note that not all questions were successful) to avoid duplication. You can find these questionnaires—including coverscreen, main interviews, exit interviews, and previous drop-offs—at http://share.cerge-ei.cz.
To formulate your questions appropriately, we recommend registering for access to the SHARE dataset at https://share-eric.eu/, downloading the data free of charge, and exploring what variables which are already available. The website also contains full project documentation, including publications, methodological materials, and detailed codebooks.
We anticipate high interest, and each contributor will likely be allocated space for a small number of questions (i.e. a topic-specific module). Questions from all fields—sociology, psychology and economics are welcome. We particularly encourage contributions that address important issues in the Czech Republic, with potential for use in academic publications, dissertations, teaching, or evidence-based policymaking.
We are especially interested in questions that are comparable with other international studies. In addition to the usual longitudinal focus, the upcoming wave will also examine cognitive abilities and — in several countries including the Czech Republic — use accelerometers to measure participants’ physical activity.
This opportunity, like data access, is provided free of charge as part of the Czech SHARE infrastructure funded by the Czech government and Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports. Please note that questions must not be related to or funded by commercial entities. Violating this rule would not only be unethical, but could also jeopardize the SHARE project as a whole.
While the primary selection criteria are quality and originality, this call is especially intended to support early-career researchers and students who may not otherwise have the opportunity to collect their own data.
Before each new wave, we contact all users and organize a workshop for those interested in submitting questions to the drop-off. If you’re interested, please send us your proposed topic, draft questions, and a short description or justification of your research idea. During the workshop, we will discuss all submissions and refine selected proposals into a working version to be submitted for approval and pilot testing.
If you know of a colleague who might be interested in participating, feel free to forward this call to them. We especially encourage forwarding this opportunity to your students.
We look forward to your participation and future collaboration.
Radim Boháček
SHARE National Coordinator – Czech Republic
CERGE-EI
Politických vězňů 7
Prague 1, 111 21
Phone: +420 775 379 336
Email: radim.bohacek@cerge-ei.cz or radim.bohacek@gmail.com
Project websites: https://share-eric.eu/ and http://share.cerge-ei.cz
You can find questionnaires and codebooks from previous waves here.
HCAP cognition data
Harmonized Cognitive Assessment Protocol
The general aim of SHARE-HCAP is to exploit the international variation of health and life circumstances in Continental Europe to identify which interactions of bio-medical and socio-economic conditions over the life course affect cognition in later life. The understanding of such life-course pathways to first mild cognitive impairment and then, possibly, dementia, should help in developing preventive early interventions.
The project will enhance our understanding how the vastly differing social, health and long-term care systems affect mental health and resulting mortality of the aging populations. This holds especially for the life circumstances in Europe since World War II which are likely to have influenced cognitive decline now at older ages. Moreover, the large variation in key policy variables, e.g. retirement age, identifies pathways from early retirement through inactivity and loss of social contacts to lower cognition, mediated by education, working environment and other socio-economic factors over the life-course.
Questionnaires
The HCAP project in the Czech Republic was administered according to the HCAP licences and questionnaires for
respondents
and
informers.
These questionnaires were translated from their English originals
respondents
and
informers.
SHARE-HCAP Data Available
Data from the SHARE-HCAP (Human Cognitive Ability Protocol) project in Wave 9 are available for download to all registered users. The data contain all HCAP modules and questions. There is also a preliminary index of mild and severe cognition decline. The final release of the SHARE-HCAP data will be harmonized with HRS-HCAP data. For more information please the accompanying dataset website.
HCAP data are available for download in the SHARE data archive.
HCAP2
SHARE-ERIC is currently proposing a longitudinal collection of HCAP2 after wave 11 on the same respondents plus an additional sample of new respondents.
Methodology
The project administers in-depth measurement of cognition according to the Harmonized Cognitive Assessment Protocol (HCAP) that has been developed for the HRS-style aging surveys supported by NIA.
HCAP consists of a recently developed battery of in-depth cognition measures. More specifically, it consists of about one hour of subject cognitive testing and a twenty-minute informant interview, both of which can be administered in the home or care facilities by survey interviewers with advanced training.
Using these data, the project will estimate prevalence rates of mild and severe cognitive impairment in the SHARE countries; compare these with HRS and other participants in the HCAP studies; and exploit the international variation of the SHARE plus SHARE-HCAP data in order to identify which interactions of biomedical and socioeconomic conditions over the life course affect cognition later in life.
The measures included in HCAP were selected by three criteria: (a) can be administered in the home by a survey interviewer in about one hour, (b) can be administered comparably and lead to comparably valid assessments in other countries where HRS-type surveys are conducted, and (c) has sufficient overlap with the 2002/03 HRS-ADAMS study that it can be used to establish trends in the prevalence of cognitive impairment in the US. Using these data, the project will estimate prevalence rates of mild and severe cognitive impairment in the SHARE countries; compare these with HRS and other participants in the HCAP studies; and exploit the international variation of the SHARE plus SHARE-HCAP data in order to identify which interactions of biomedical and socioeconomic conditions over the life course affect cognition later in life.
Countries: The project will be implemented in five SHARE countries (Denmark, Czech Republic, Germany, France, Italy) in a stratified study sample of 2,500 SHARE panel respondents. The start of the fieldwork is planned by early 2022. Versions of HCAP will also be conducted in the US, Mexico, India, China, and South Africa.
For more information on the HCAP Network visit: https://hrs.isr.umich.edu/data-products/hcap
geoSHARE
We are currently processing geographical information from all SHARE respondents, including life history data, at NUTS2 and NUTS3 levels. The data will be available with restricted access in order to comply with GDPR privacy rules.
geoSHARE data
In collaboration with our Italian colleagues from Ca’ Foscari University in Venice, we have processed all data on the locations of respondents during interviews in each wave of SHARE data collection.
We have combined this data with information about their life events from the DN questionnaire and information about their parents, children, and family.
The result will be a detailed history of the respondent’s geographical location from birth to the last interview in the SHARE study.
The publication of the data itself must undergo a legal review to ensure that all conditions for personal data protection and GDPR rules are met. SHARE-ERIC is responsible for this. We expect the data to be published at various levels of open access in 2026.
Methodology and documentation:
You can download the results of our work as a working document.
Location of respondents in individual waves Working document
Geographic data: location of respondents in life history Working document
Geographic maps:
Location of respondents in life history
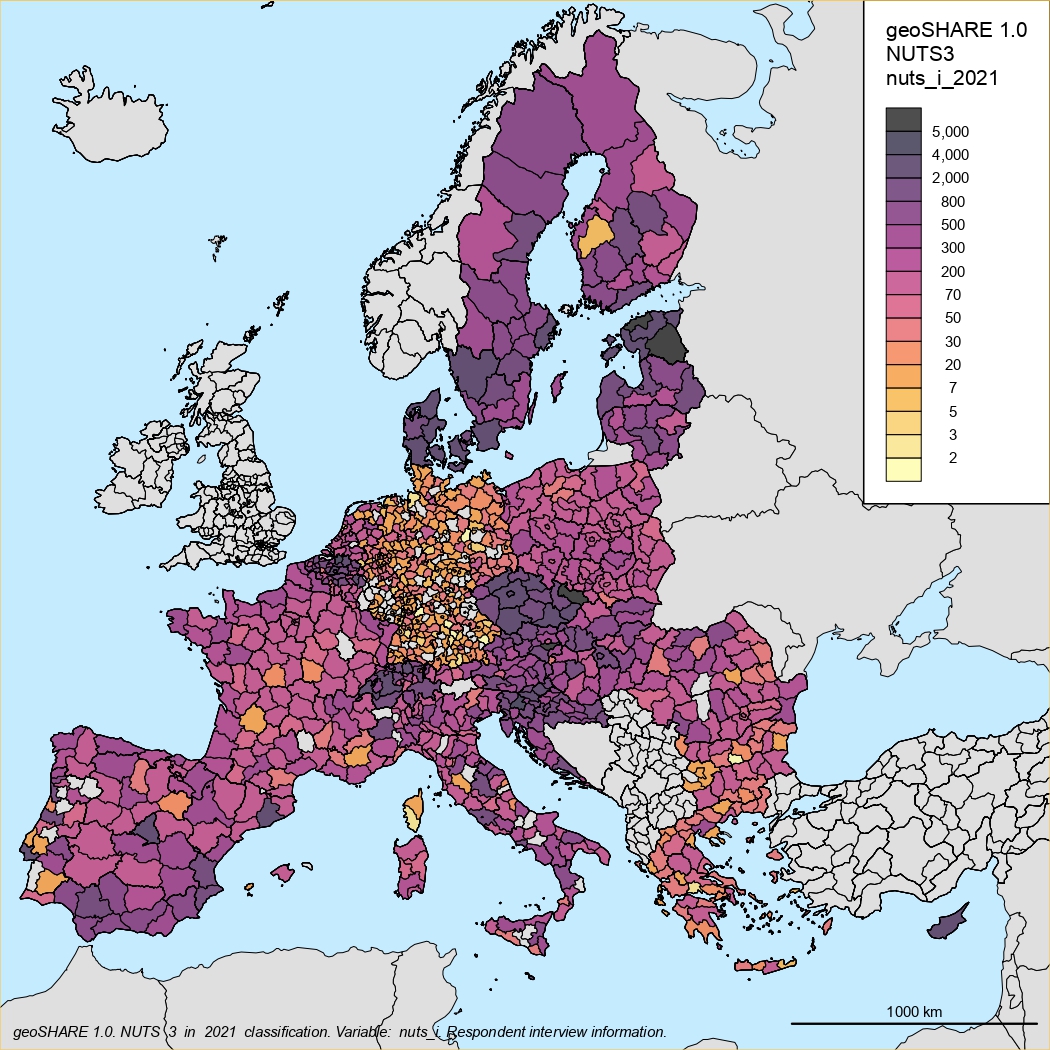
NUTS3 classification
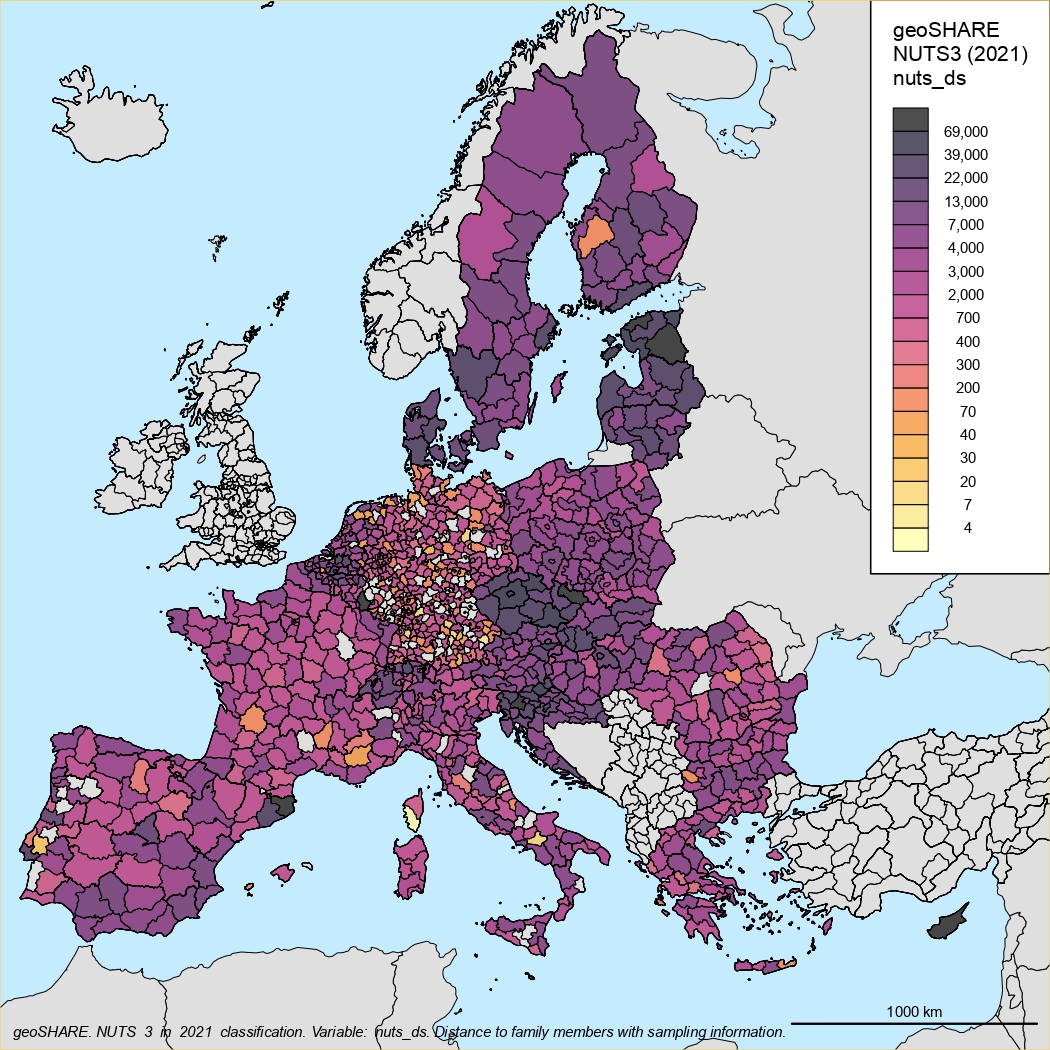

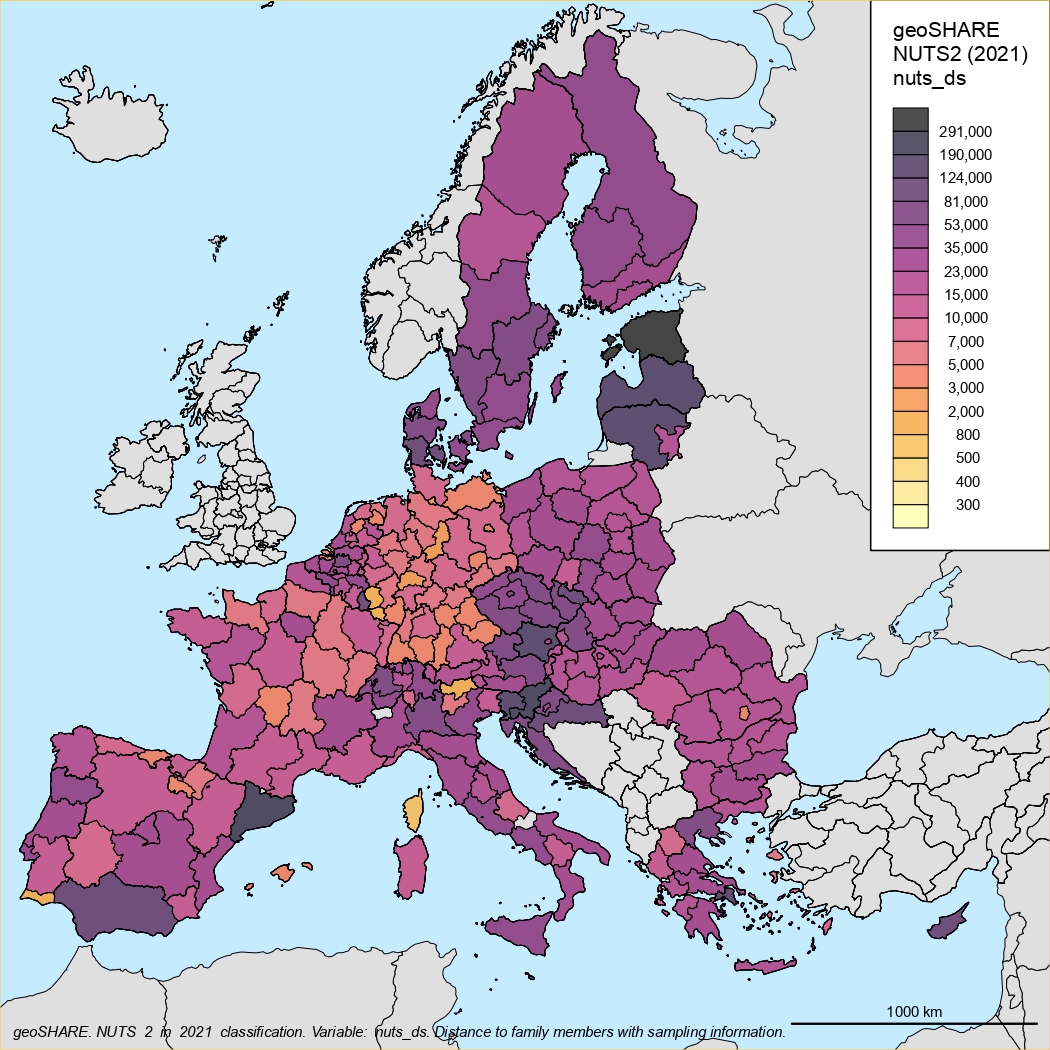
NUTS2 classification

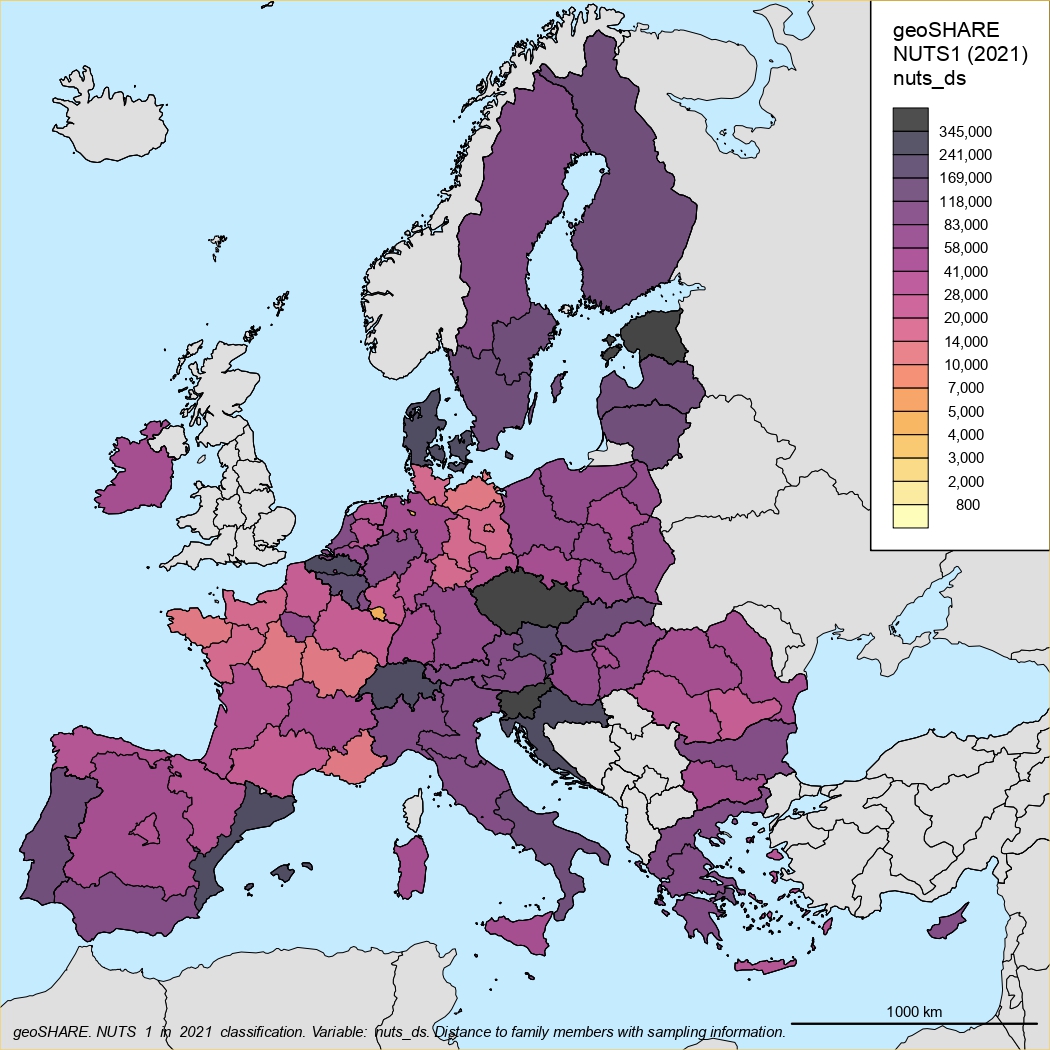
NUTS1 classification

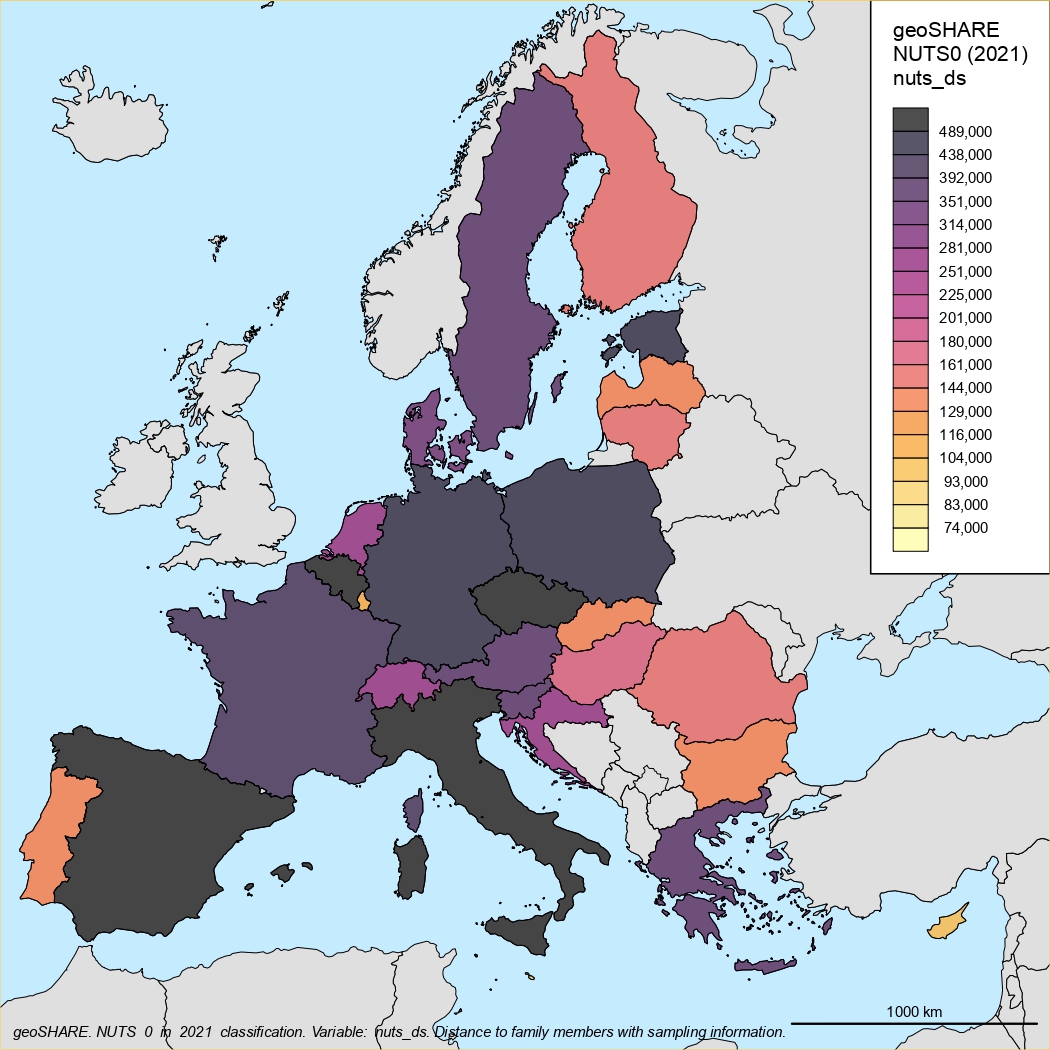
NUTS0 classification

Location of respondents during data collection in individual SHARE waves
NUTS3 classification

NUTS2 classification
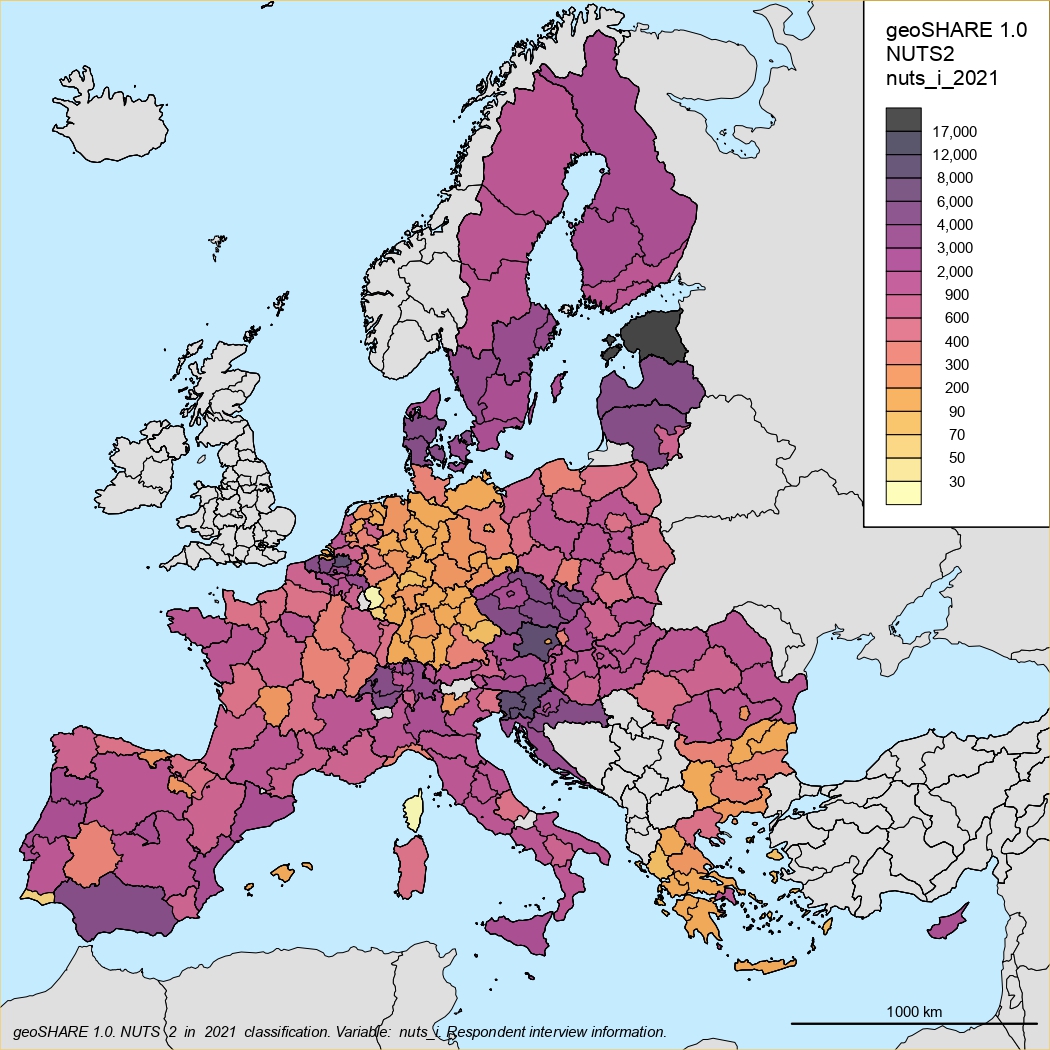

NUTS1 classification
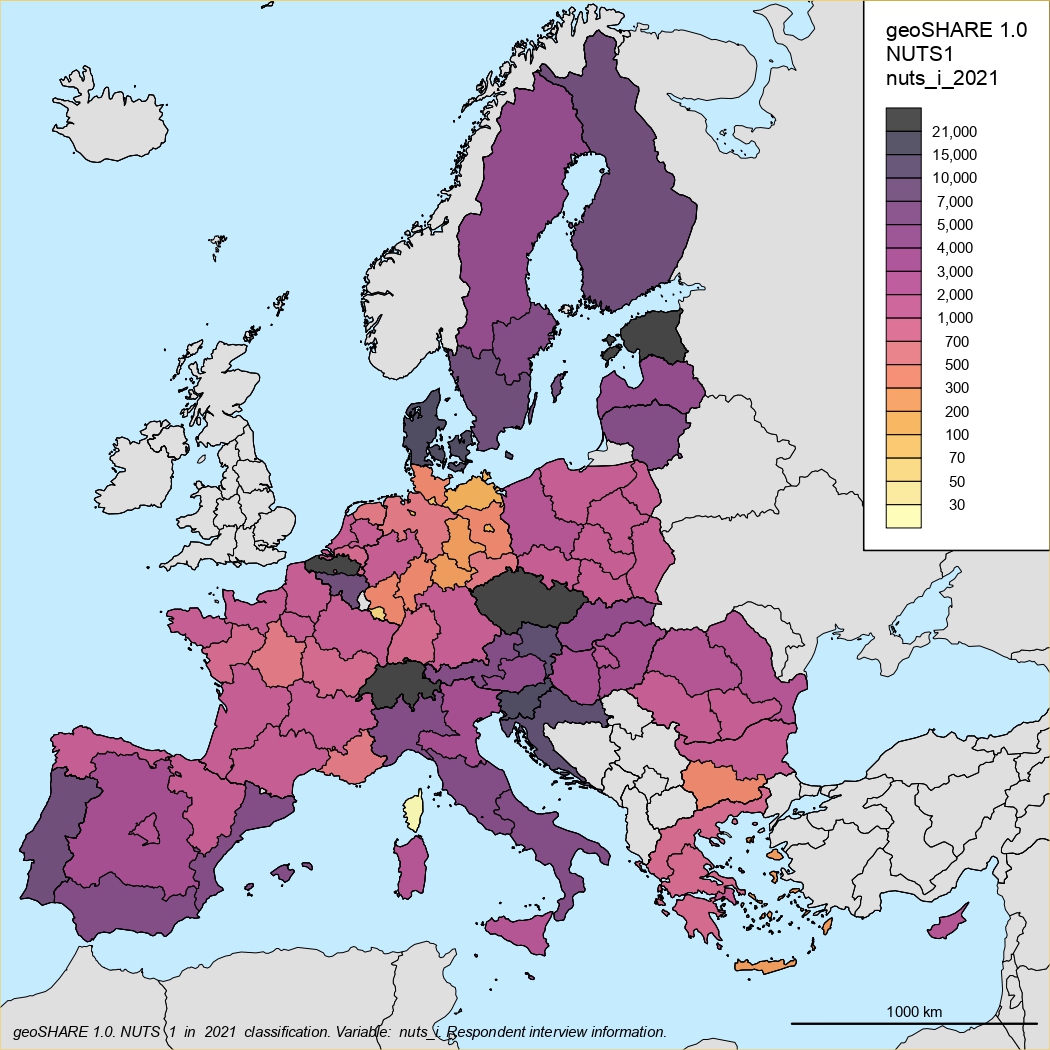

NUTS0 classification
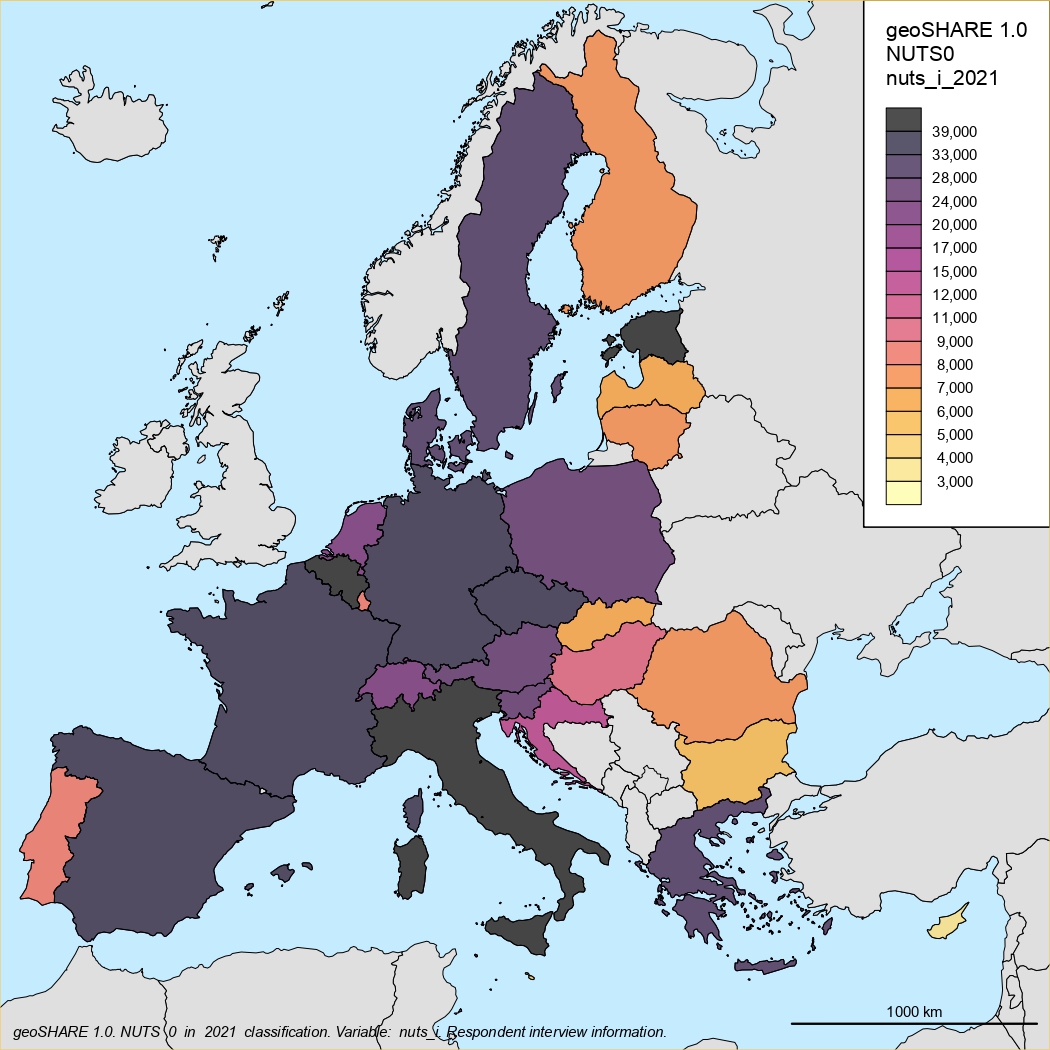

neuroSHARE
The neuroSHARE Remote Study in Switzerland
The original neuroSHARE Study will be adapted to a remote version for a data collection in Switzerland in wave 11. The project will be expanded to new tests of facial motion and hearing. The cost efficiency of the neuroSHARE Study will be substantially improved by the remote, self-administered version of all tests for a smartphone (speechtest, facial motion, and hearing) and website (sleep questionnaire) version of the tests. Data for the smell test will be collected by a olfactory papers sent by mail. The application will be developed by a joint collaboration with the First Faculty of Medicine at Charles University, the Faculty of Electrical Engineering at the Czech Technical University, and the University of Lausanne, our SHARE-CH partners. The project is generously supported by the Czech-Swiss Partnership and Funds (CZ-CH Funds).
The neuroSHARE Study in the 10th wave of SHARE
The tenth wave of the SHARE project focuses on collecting neuromarkers in the neuroSHARE project, consisting of a smell test, speech test, and questionnaire on REM sleep quality, in collaboration with the First Faculty of Medicine of Charles University and the Czech Technical University in Prague.
Three short tests are conducted immediately after the main questionnaire is completed. Speech, smell, and sleep disorders are important early markers for Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases, as well as depression. This is a unique project being tested for the first time on a large population sample. The aim of the project is the early diagnosis of these diseases, their timely treatment, and the prolongation of quality of life.
In the eleventh wave, we plan to collect even more comprehensive objective data, known as biomarkers. This project will be carried out in collaboration with the large RECETOX research infrastructure at Masaryk University in Brno.
neuroSHARE - Measurement of Neurodegenerative Diseases in SHARE Survey
Speech, olfactory (smell) and sleep dysfunctions belong among the earliest and most important signs of neurodegenerative diseases and depression. In Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease, decreased sense of smell precedes the occurrence of motor and cognitive symptoms by years or even decades. Similarly, prosodic changes of speech are evident already in the prodromal stages of both diseases. Finally, the strongest risk factor for dementia or later development of Parkinson’s disease is REM Sleep Behavior Disorder.
This project implements the olfactory and speech tests on the sample of Czech respondents in the SHARE (Survey of Health, Ageing, and Retirement in Europe) project, the largest representative panel study of the population aged 50+. The measurements take place in wave 10 (2024-2025) in the Czech Republic (4,000 respondents). The sleep disorder is be captured by a short validated questionnaire. Respondents with abnormal test results are invited for medical examination.
The project is financed by the LM and LX grants from the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic. The finances are allocated for years 2024-2025 corresponding to wave 10 of the SHARE project. These finances are grant and project specific and cannot be used for other purposes and cannot be transferred to subsequent years.
Together, these tests provide very robust biomarkers of neurodegeneration scalable to larger populations. All tests are inexpensive, noninvasive, and can be performed and assessed repeatedly. The project is the first implementation on a large, representative sample of respondents and provides unique insights and opportunities for early diagnosis and treatment in the ageing European population. The output is a part of the open-access data available to all registered users of SHARE. The methodology is be piloted in wave 10 in the Czech Republic and later used in other countries in Wave 11.
Novel Biomarkers for Early Detection of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Introduction
Speech, olfactory (smell) and sleep dysfunctions belong among the earliest and most important signs of neurodegenerative diseases. In Parkinson’s disease (PD) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD), decreased sense of smell precedes the occurrence of motor and cognitive symptoms by years or even decades. Similarly, prosodic and/or linguistic changes of speech are evident already in the prodromal stages of both diseases. Finally, the strongest risk factor for the development of PD and dementia with Lewy bodies is rapid eye movement (REM) Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD). Thus, patients with isolated RBD represent a special case of prodromal alpha-synucleinopathy with a very high rate of conversion to a manifest neurodegenerative disorder. However, while sensitive screening tests for speech, olfactory, and sleep dysfunction are available, they often lack specificity when administered individually.
An intriguing novel approach for early, accessible detection of neurodegeneration involves analyzing altered speech and smell patterns in combination. These methods are non-invasive, inexpensive and easy to administer, even from subject’s home, making them practical for screening large populations for early signs of neurodegeneration. Speech is highly susceptible to neurodegeneration, providing a window into brain health. It reflects cognitive-linguistic and motor-execution performance but also mood and emotions via facial expression, which are all affected by neurodegeneration. Olfactory dysfunction, such as impaired odor identification and detection, often appears years before other symptoms. The brain areas responsible for processing smell, including the olfactory bulb, entorhinal cortex and hippocampus, are also some of the first regions affected by alpha-synuclein-related and Alzheimer’s-related pathology, respectively. Studies have shown that people with reduced olfactory abilities are at a higher risk of developing cognitive impairment, AD, and PD.
The largest multinational multilanguage trial performed by our team in a large sample of subjects with isolated RBD and early-stage PD showed that speech impairment severity assessed via acoustic analysis was progressive in both PD and RBD over one-year follow-up (Rusz et al. 2021). Subsequently, dysprosodic speech disorder was found in isolated RBD subjects with impaired olfactory function before the nigrostriatal dopaminergic transmission was affected (Rusz et al. 2022), indicating speech disorder as one of the earliest signs of PD occurring already in the Braak stage 2. Similar findings related to changes in prosody have been observed across variety of neuropsychiatric disorders including AD, other dementias, schizophrenia and other diseases (Rusz et al. 2024).
In addition, impaired facial expression is commonly observed in majority of neurodegenerative diseases such as AD and PD. Altered facial expression is one of the earliest distinct motor manifestations of PD (Fereshtehnejad et al. 2017). We recently showed that automatic video-based analysis of facial expression might detect PD early (Novotny et al. 2022).
The investigation of language function, a core cognitive domain in mild cognitive impairment, might provide valuable information about phenoconversion to dementia (Boschi et al. 2017). Indeed, objectively derived linguistic features of spontaneous speech were able to detect preclinical stages of dementia (Beltrami et al. 2018). The high clinical relevance of natural language and speech assessment has been recently demonstrated by our team in patients with isolated RBD. This trial showed for the first time that language screening is able to identify and distinguish patients who will later develop dementia or parkinsonism (Subert et al. 2024). In particular, language abnormalities were strong predictors of dementia with the highest hazard ratio reported in literature so far (approximately 100). These results were based only two minutes of spontaneous speech, thereby strongly supporting linguistic measures as ideal candidate markers to be employed in selecting patients for screening and future neuroprotective trials.
neuroSHARE Project Protocol
The combination of a standard olfactory test, a specially designed innovative speech test, and the REM Sleep Behavior Disorder Screening Questionnaire (RBDSQ) are currently tested in the pilot study of neuroSHARE in Wave 10 (2024-2025) in the Czech Republic with 4,000 respondents in the Survey of Health, Ageing, and Retirement in Europe, the largest representative panel study of the population aged 50+. Respondents with abnormal test results are invited for an expert medical examination. The open-access data available to all registered SHARE users.
-
Fieldwork Procedures: The neuroSHARE project is introduced to all panel and refresher respondents immediately after the completion of the main interview. Respondents are asked to provide their consent with testing and the medical examination.
-
The speech test is administered by an application on the interviewer’s computer with attached microphone. There are five tasks in the speech test: prolonged phonation, repeated syllable, reading a text, retelling of a fairy tale, and a monologue. The test is language-independent. The recorded wav files are analyzed into several parameters representing key motor and cognitive speech abnormalities such as monopitch, monoloudness, harshness, impaired timing, content richness, vocabulary range, sentence development and others.
-
The smell test is a standard olfactory assessment, previously used in HCAP and HRS, involving Sniffin’ sticks test to measure both smell identification and olfactory threshold. The sleep test - RBDSQ - is an internationally validated self-administered questionnaire. The neuroSHARE questionnaire also contains additional questions related to factors that may influence speech, smell and sleep. The total duration is about 25-30 minutes.
-
Harmonization and data delivery: Smell test is harmonized with the HRS and ELSA smell tests. Data are delivered for merging to the SHARE panel data with full documentation. Transfer, analysis, and storage of audio files and other data materials comply with GDPR requirements.
-
Medical examination: Respondents with abnormal findings (around 5 percent of respondents) in smell and speech test and abnormal RBDSQ score are invited for an expert medical examination and validation at the Department of Neurology, First Faculty of Medicine, Charles University.
-
The neuroSHARE project: is the first implementation of these tests on a large, representative sample of respondents and provides unique insights and opportunities for early diagnosis and treatment in the ageing European population. Based on the pilot study results, additional measurements might be investigated (potential long-term neuropsychiatric burden associated with depression and olfactory dysfunctions related to the Covid-19 pandemic).
-
Coordination and research team: SHARE-CZ (Radim Bohacek), First Faculty of Medicine at Charles University (Petr Dusek), Czech Technical University (Jan Rusz, Tereza Tejkalova, Vojtech Illner, Tomas Kouba).
-
Central coordination is administered by the SHARE-ERIC and the SHARE Berlin Institute. The neuroSHARE project has obtained all required approval from the Ethical Committee at the First Faculty of Medicine of Charles University. It has been supported by SHARE-ERIC Management Board, the SHARE-ERIC Scientific Monitoring Board and its chair Arie Kapteyn (USC), and the SHARE-ERIC Director, Prof. David Richter.
-
neuroSHARE in Switzerland: The methodology will be shared with other countries in the SHARE project, first with the Swiss team of SHARE-CH at the University of Lausanne in Wave 11.
For more details, see:
nutriSHARE
FFQ and 24HR Nutrition Survey in SHARE-CZ
Between wave 10 and wave 11, in the fall 2026, SHARE-CZ will collect detailed data on nutrition.
Both the FFQ (Food Frequency Questionnaire) and 24HR (24h Recall Questionnaire) are standard questionnaires used in other major surveys (NICOLA, ELSA, HRS and NHANES variants).
This research project is developed in collaboration with the First Faculty of Medicine, Charles University and General University Hospital.
Dr. Tereza Vagnerova is the scientific coordinator at the Department of Geriatrics and Internal Medicine.
Background and Aims
Diet is a key, modifiable determinant of healthy ageing, affecting cardiometabolic risk, frailty, sarcopenia, cognitive decline, and disability trajectories. However, robust diet-health analyses in ageing cohorts require dietary exposure measures that are (i) sufficiently detailed for nutrient- and food-group analyses, (ii) comparable across countries and survey waves, and (iii) feasible in older populations with heterogeneous digital skills and health constraints.
SHARE is uniquely positioned to address diet-related research questions in later life because it combines repeated, harmonized measures of health, function, socioeconomic status, and social networks across many European countries. Yet, diet has historically been under-measured in SHARE relative to its importance for life-course epidemiology. Implementing a Czech Nutrition Survey as a country-specific sub-project linked to SHARE Wave 11 creates high scientific value - it enables integration of dietary exposures with rich SHARE phenotyping and supports cross-country harmonization by aligning with instruments already used in other ageing studies.
Primary research aims of the Nutrition Survey
- To quantify key dietary exposures in adults aged 50+ in the Czech SHARE sample, including foods, nutrients, and dietary patterns, and to link these exposures with SHARE’s longitudinal health, functional, and socioeconomic outcomes from a life-course perspective.
- To enhance cross-study and cross-country comparability of dietary data within ageing research by aligning nutritional outputs with established European population studies and harmonized food and nutrient constructs.
- To improve the validity and interpretability of diet-aging associations by addressing known sources of measurement error in dietary assessment.
Objectives and Content of the Nutrition Survey
Including the collection of newly developed survey measures of nutrition in SHARE data provides important scientific value as it opens up multiple research possibilities:
- Diet-ageing trajectories: modeling associations between dietary exposures and longitudinal changes in functional status, frailty, cognition, morbidity, and health service use (leveraging repeated SHARE measures).
- Dietary patterns and inequality: analyzing dietary patterns/scores (e.g., PCA-derived patterns, cluster solutions, Mediterranean-style or other diet indices) in relation to socioeconomic position, social networks, and regional variation within an ageing population.
- Methodological research: quantifying and correcting measurement error (under-reporting, selective non-response, mode effects) and evaluating feasibility of digital dietary assessment in older adults, including mixed-mode solutions.
The Nutrition Survey is based on existing, validated, and internationally used nutrition instruments:
Questionnaires
-
Food Frequency Questionnaire (EPIC-Norfolk FFQ; EPIC-based) - captures habitual intake through a structured list (130 food lines) with standard frequency categories and portion conventions, suitable for long-term exposure ranking and trend comparisons.
Download the FFQ questionnaire here.
-
24-hour dietary recall (MyFood24; 2 administrations) - captures detailed day-level intake (one weekday + one weekend day) with automated nutrient analysis, enabling meal-pattern outputs and more granular food group exposure estimates; validation evidence supports its use in large studies as a scalable alternative to interviewer-based 24HDR.
Link to 24HR myfood harmonized questionnaires.
Both questionnaires will be in a website mode with optional CATI mode for respondents unable or unwilling to use the website mode.
Links to other nutrition studies
bioSHARE
bioSHARE: Collection of biomarkers in SHARE
Biomarker analyses have become one of the most important innovations in micro data collections in major surveys on ageing. Biomarkers improve the measurement of health status by providing information on health conditions that are not easily observed and reported by respondents. They also help to elucidate pathways connecting social and environmental factors to broad health outcomes. Biomarkers obtained from the blood include cytokines, immune system markers, molecular and cellular markers of aging, and gene expression. Coded biomarkers are available as restricted-access data linked to main longitudinal data for each respondent while the assays are stored in a long-term repository to take advantage of future scientific and technological developments.
Biomarkers have been collected in all major longitudinal ageing surveys. The Health and Retirement Study (HRS) and the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (ELSA) collected biomarker data in 2014-2016, including venous blood samples. Twelve countries in SHARE-ERIC collected dried blood spots in wave 6 in 2014/15. Unfortunately, the Czech Republic could not join in this biomarker collection due to financial constraints and legal restrictions on fieldwork implemented by certified medical staff.
Collection of Biomarker Data in the Czech Republic: A Synergy of SHARE-CZ and RECETOX
In order to redress this gap in Czech SHARE data, a synergy between two large research infrastructures, SHARE-CZ and RECETOX at the Masaryk University in Brno, is planned for SHARE wave 11 in 2027. In full compliance with the legislation, in the Czech Republic biological samples will be collected from all respondents through sub-contracted medical facilities and analyzed by professional laboratory staff at RECETOX. Coded data will be merged with the longitudinal SHARE-ERIC data. The collection and methodology will be compatible with HRS, ELSA, SHARE-ERIC other biological sample collections. This new database, linked also to the SHARE Harmonized Cognitive Assessment Protocol (HCAP) study, will represent a unique database not only in the SHARE-ERIC but also in European and world research. This synergy will put Czech SHARE data on the forefront of world research connecting biomedicine and social sciences, opening opportunities for Czech researchers in scientific outcomes and publications.
In the planned biomarkers collection, the most important samples are venous blood (VBS) and dried blood spots (DBS). Additional measured data will include the following variables: weight, height, waist circumference, hip circumference; blood pressure and pulse; ECG electrocardiography (by a portable ambulatory machine by CardioSecur); vision, hearing, smell, speech, and balance tests; TBC vaccination mark on shoulder; lung functions as forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume (FEV), and/or peak flow (PF). In addition, respondents will be asked to bring their medications that will be scanned by QR/barcode technology, photographed, and listed. These are the essential biomarkers that can be collected in SHARE survey conditions. As in other biomarker surveys, respondents will be informed on their test results and alerted if any of the markers is abnormal.
Biomarkers and Exposomes: In Wave 11 in 2027, all respondents in the Czech Republic will provide venous blood samples and other objective measures. Additional linkages will be provided for exposome data. Both biomarker and exposome data will be harmonized with HRS, GECC and other projects. Biomarker collection will be administered by RECETOX RECETOX Laboratories at Masaryk University, and the future coordinator of EIRENE-ERIC.
Accelerometer Study in Wave 8 in the Czech Republic
In SHARE Wave 8, data on physical activity were collected by using accelerometers. A subsample of the panel respondents were asked to wear the device (Axivity AX3) for eight consecutive days (day and night) on their upper thigh.
The SHARE accelerometer study was conducted in ten countries: Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Poland, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden.
A detailed description of the study is available in
the SHARE Wave 8 Methodology Volume.
Raw accelerometer data is processed with ActiPASS and GGIR and resulting measures are available in the Wave 8 gv_accelerometer modules. Variables based on ActiPASS provide information on postures and activities, e.g. sitting, lying, standing, walking, as well as intensity categories, i.e. sedentary, light, moderate, and vigorous activity. Activities detected by ActiPASS are available as 1-seconds intervals. Provided metrics based on GGIR include vector magnitude (ENMO), intensity gradient, and LXMX measures. Additional datasets with information on acceleration on epoch level (5 seconds) for each participant are available.
Raw sensor data is available upon request at the SHARE-ERIC Berlin Institute.
For further details see SHARE wave 9 Release Guide.

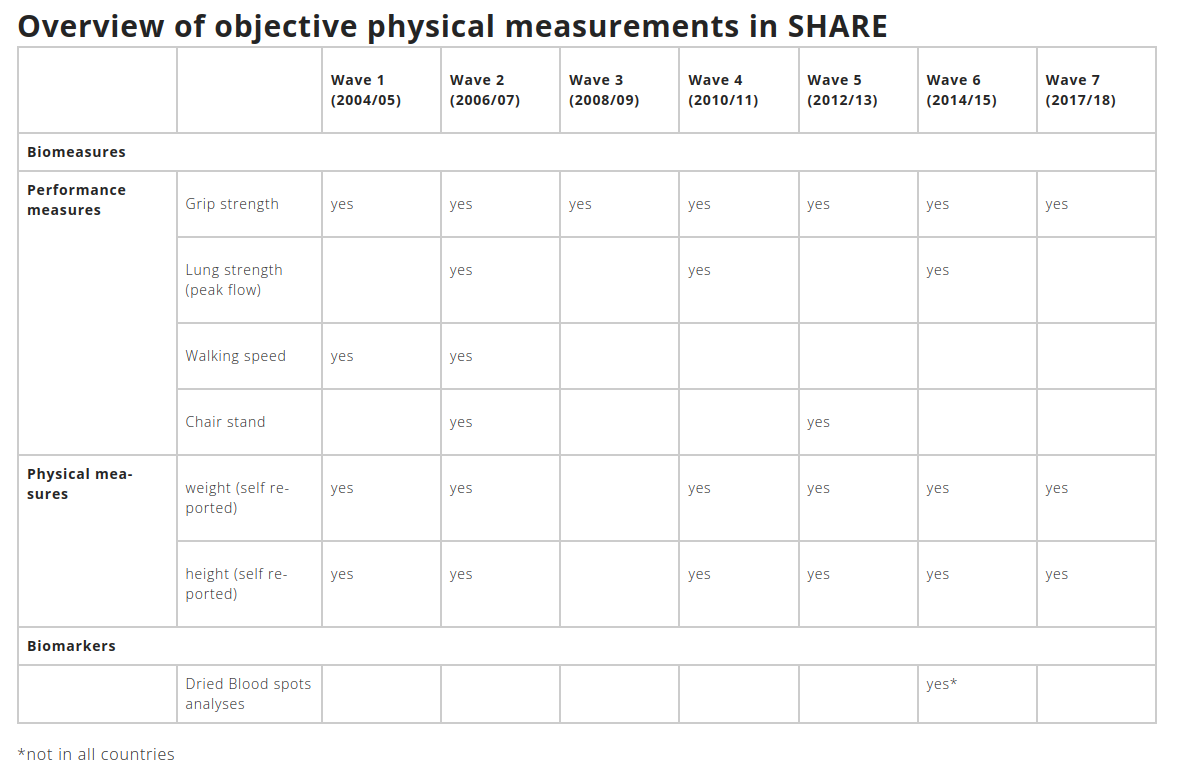
Physical measures in all waves
All waves of SHARE include objective health data (biomeasures) in form of physical performance measures: grip strength, walking speed (both strong predictors of future disability), peak flow (associated with health conditions, including dementia) and the so-called chair stand measurement (its result is a predictor of subsequent disability or hospitalization). Additionally, we ask respondents for their height and weight. Not all of the listed measures are collected in every wave, for more details see the table below.

SHARE Dried Blood Spots (DBS) data
Release 1-0-0 of SHARE Dried Blood Spots (DBS) data is the first release with seven blood biomarkers serving as additional objective measures of health. Twelve countries participated in the DBS sample collection during wave 6.
Dried Blood Spot (DBS) project fosters our understanding of cross-national differences in health and their causes, especially evaluating differences in health care systems, health behaviors, and historical life circumstances. Understanding differences and causes requires comparable measurements of health which do not suffer from cross-national differences in data collection and reporting styles. In this respect, analyses of blood samples became the minimum standard of objective health measurement. SHARE, the European counterpart of HRS, has therefore collected dried blood spot (DBS) samples from about 27.000 respondents aged 50 and older in twelve Continental European countries.
The project has four specific aims:
- Capitalize upon the expertise of the laboratory at the University of Washington by having the full set of DBS collected in SHARE wave 6 assayed for the lipid panel and type-2 diabetes mellitus biomarkers relevant to general health and cognitive decline.
- Link the laboratory analyses with the SHARE functional and subjective health, demographic, social, and economic data, create a user-friendly database and archive it.
- Harmonize the data obtained from the assays of SHARE DBS, ELSA VB and HRS DBS and VB.
- Use these data to perform statistical analyses on the relationships between cross-national differences in health, economic, work and social circumstances, health behaviors and health care interventions.
More information about the DBS data collection.
easySHARE
easySHARE (version 9.0.0)
easySHARE is a simplified version of the SHARE database, designed primarily for researchers and students who are just starting with the analysis of complex longitudinal data.
While the main SHARE database is split into dozens of files by wave, easySHARE compiles information on all respondents across all countries and waves into a single dataset.
The data structure is much more user-friendly – information on respondents and their households is merged across all waves. Missing values are clearly classified and the dataset includes many derived variables (e.g., education level according to ISCED, health index, functional limitations, demographic and economic indicators).
easySHARE is fully compatible with other ageing studies (such as HRS and ELSA) and supports group registration for university teaching purposes.
Data Structure
The data are available as a single ZIP file containing information on respondents from all participating countries since 2004 (including the Czech Republic from 2006 onward). This format is ideal for teaching panel data analysis and for cross-country comparisons.
The archive also includes a Stata script used to create the easySHARE file from the main database – allowing users to trace how the variables were derived and linked, and to adapt the code for their own research.
Access to Data
The easySHARE dataset is available to registered users through the SHARE Research Data Center. Login credentials are the same as for the main database. The same terms of use apply.
Teachers can use a simplified registration form to grant students access for educational purposes.
More info: data access
Free Data Analysis in R
Guide to working with easySHARE (PDF).
easySHARE data are also available for analysis in R programming language:
http://www.r-project.org/
abmSHARE
Epidemiological Model abmSHARE
SHARE has become ever more important as a tool for evidence-based policy making due to the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic. SHARE is the ideal database to study the non-intended socio-economic and health consequences of the epidemiological containment decisions and the long-term effects of the COVID-19 pandemic due to its life-course and multidisciplinary approach combining health with socio-economic data. The European Commission supports a new COVID-19 research project (SHARE-COVID19) with funds provided by Horizon 2020 and the Coronavirus Global Response.
abmSHARE is an agent-based (also called individual-based or microsimulation) epidemiological spatial model adapted to SHARE and Eurostat data. It was developed for the Horizon SHARE-COVID19 project. The model was developed in collaboration with the Faculty of Biomedical Engineering at the Czech Technical University and the DNAi Ltd. programmers.
The goal of the abmSHARE model is to simulate the spread and impact of Covid-19 and similar epidemiological scenarios through realistic populations, across multiple regions, and under different intervention policies (like lockdowns, vaccines, or testing). The abmSHARE model extends the open source Covasim model into geospatial simulation and incorporation of external data.
Key Features:
- Multi-region modeling (e.g. NUTS‑2 units with inter-regional travel)
- Realistic population dynamics: households, schools, workplaces
- Simulates NPIs, testing, vaccination, reinfections
- Inputs external data from SHARE, Eurostat, or other sources
- All settings can be changed and configured via configurable simple JSON/CSV inputs
abmSHARE in the Google Colab Notebook
The abmSHARE model can be run directly in your browser inside the Google Colab notebook.
Please click abmSHARE model in the Google Colab to open the Google Colab abmSHARE site at Google Colab. There you can follow a detailed documentation and run the model. There is no need for any installation. We would be very grateful for any comments and suggestions.
The abmSHARE model is built on Covasim (COVID-19 Agent-based Simulator), an open-source agent-based model developed by the Institute for Disease Modeling available at https://github.com/InstituteforDiseaseModeling/covasim, and build with related SynthPops, an open-source synthetic population constructor developed also by Institute for Disease Modeling available at https://github.com/InstituteforDiseaseModeling/synthpops.
The model is written in python and can be adapted by users to suit their research questions and local context by specifying detailed data on population (age structure, mobility, contacts) and the epidemic (diagnosed cases, hospitalization, deaths). As in the original Covasim model, abmSHARE cab be used to explore theoretical research questions or to make projections, its main purpose is to evaluate the effect of different interventions on the epidemic. These interventions include physical interventions (mobility restrictions and masks), diagnostic interventions (testing, contact tracing, and quarantine), and pharmaceutical interventions (vaccination).
abmSHARE extends the original Covasim model in two important dimensions: it allows epidemiological simulations across geographic regions (countries, NUTS) and is able to input external data as parameters for characterizing these regions in terms of their population, policies, or socio-economic conditions, for example. The abmSHARE includes all information of the Covasim model in region-specific geospatial environment on age structure and population size in each region; realistic transmission networks in different social layers, including households, schools, or workplaces; age-specific epidemiological outcomes; and viral dynamics and transmissibility. The abmSHARE model allows for region-specific policy interventions such as non-pharmaceutical interventions (physical distancing, lockdowns), vaccinations, testing, contact tracing and quarantine, all with detailed time structure and other factors.
We are very grateful to our colleagues who collaborated on the project:
Fakulta biomedicínského inženýrství ČVUT,
DNAi Ltd,
Pireus University,
Radim Krupička, Tomáš Krajča, David Jirsa, Markéta Pechholdová, Alevtina Kuznetsova,
Tom Dasaklis,
Nikolaos Rachaniotis,
Platon Tinios.
The abmSHARE model has been built for the Horizon SHARE-COVID19 project.
For further information on the model, how to become a user, for collaboration, please contact the SHARE-CZ team at 📧 radim.bohacek@cerge-ei.cz.
SHARE Covid-19
SHARE-Covid19 CATI Project
SHARE collected two special surveys on Covid19 both in CATI mode. The first survey was collected in June-August 2020, the second CATI was collected in summer 2021.
In addition, the Czech Republic added an additional CATI-CZ Covid19 survey in October-December 2020.
All three surveys have a panel structure with repeated questions to capture changes in our respondents lives during the pandemic. All CATI Covid19 data have been linked to main longitudinal SHARE data.
CATI1, CATI-CZ and CATI2 data have been already released in open access regime.
More details can be found at SHARE-Covid19 website.
Corona Survey Release Guide is available for the whole sequence of SHARE COVID19 surveys.
Understanding non-intended consequences of epidemic control decisions to contain the pandemic
The non-intended consequences of the epidemic control decisions to contain the COVID-19 pandemic are huge and affect the well-being of European citizens in terms of economics, social relationships and health: Europe is experiencing the largest recession since World War II, social contacts have been interrupted and people avoid seeking medical treatment in fear of infection.
The overarching objective of the SHARE-Covid19 project is to understand these non-intended consequences and to devise improved health, economic and social policies. In our policy recommendations, we strive to make healthcare systems and societies in the European Union more resilient to pandemics in terms of prevention, protection and treatment of the population 50+, who represent the most vulnerable segment of the population.
The project aims to identify healthcare inequalities before, during and after the pandemic, to understand the lockdown effects on health and health behaviours, to analyse labour market implications of the lockdown, to assess the impacts of pandemic and lockdown on income and wealth inequality, to mitigate the effects of epidemic control decisions on social relationships and to optimise future epidemic control measures by taking the geographical patterns of the disease and their relationship with social patterns into account as well as to better manage housing and living arrangements choices between independence, co-residence or institutionalisation.
The project pursues a transdisciplinary and internationally comparative approach by exploiting the data sources of the SHARE research infrastructure. It covers all EU Member States. The Max Planck Society is in charge of the project coordination. The project started on 1 November 2020 and will end on 30 October 2023
Interactive database
The SHARE Data & Documentation Tool is a web application developed by CentERdata (Institute for Data Collection and Research) in collaboration with SHARE Central at the SHARE Berlin Institute. For researchers, the tool serves as a fast, customizable, and user-friendly web interface for browsing and searching the SHARE metadata.
One of the key features of the system is the ability to generate codebooks for all currently available waves and modules of the SHARE project in PDF format. This allows researchers to get an initial overview of the dataset’s content and case numbers without needing to download the data.
The “Browse Publications” tab includes all publications reported to SHARE Central, such as journal articles, books, book chapters, and other types of work like discussion papers or theses.
The “Search” function helps you quickly locate the information you need — whether across all areas, or specifically within datasets, questionnaires, or publications.
The tool is available at:
https://www.share-datadocutool.org/
You can search for SHARE publications and survey content


expoSHARE
We are currently preparing a proposal for cooperation with the research infrastructure EIRENE at Masaryk University within the SIRENE project in the Horizon program. The goal of the project is to connect SHARE data to exposomes.
What is the Human exposome?
People differ in their genetic predispositions, which account for 20–70% of the likelihood (depending on the disease) of staying healthy or developing chronic conditions. Health is shaped by the interaction between genetic (i.e., the human genome) and non-genetic factors, collectively called the exposome.
These factors include the quality of natural, work, and home environments; exposure to toxic substances; nutrition and dietary habits; lifestyle choices; physical activity; the use of alcohol, drugs, or medications; smoking; socioeconomic status; and psychological stress. Understanding how these factors interact is critical for advancing precision medicine and prevention. Unlike genetics, many of these factors are modifiable, offering significant opportunities for improving population health.
Assessment of Risks from Chemicals
Exposure to toxic chemicals is an important constituent of the exposome concept. Exposome research will generate new methodologies, datasets, and tools for assessing chemical exposures and associated risks applicable to chemical regulation, risk management, and health protection. In this context, the efforts of EIRENE and PARC (the Partnership for the Assessment of Risks from Chemical) are well aligned, working synergistically to advance our understanding and management of chemical exposures.
Contribution to the One Health concept
The exposome concept is not human-centered and can be applied to other species and whole ecosystems, thus providing the tools for implementing the One Health concept.
SPLASH Database
Social Policy Archive for SHARE (SPLASH)
The Social Policy Archive for SHARE (SPLASH) provides the necessary macro and contextual data (e.g. regarding political, economic, and societal environments) facilitating comparative analyses of social policies over space and time using SHARE and other microdata sources.
SPLASH Website can be accessed at https://splash-db.eu/
More specifically, the Data section gives access to contextual quantitative indicators based on official statistics and research outcomes. In the Policy section users will gain access to standardized information about policy changes and their legal supporting documents over time; the records have been compiled from the Population and Policy Database (PPD) and the Population Europe Resource Finder and Archive (PERFAR), which was last updated in 2016.
In addition, SPLASH will provide access to a data map of quantitative and qualitative external sources complementing the contents offered by the two sections.
In terms of content, SPLASH is focused on resources covering European countries organized by the following topics:
- Education
- Family & Children
- Health
- Migration
- Living Conditions
- Work & Retirement
Job Episode Panel
The SHARE Job Episodes Panel (JEP) is a generated dataset based on information of Wave 3 (SHARELIFE) and Wave 7 of SHARE. It comes in the form of a retrospective long panel. The JEP contains the labour market status of each respondent throughout her/his life. Such a retrospective panel is useful when studying the potential effects of early childhood conditions on conditions in later life or when the focus of the analysis is a low frequency phenomenon barely captured by the regular panel waves of SHARE. The JEP offers the opportunity to study life-cycle processes and the accumulative effect of important events over the life-course recorded in Wave 3 and in Wave 7. Moreover, the JEP dataset can be complemented by information about the institutions, public policies and macroeconomic conditions individuals are confronted with in the course of their lives.
A detailed description of the methodology and assumptions underlying the construction of the dataset is available in the SHARE working paper 36
and SHARE working paper 42.
The latest Release of the SHARE JEP is based on Release 9.0.0
linkSHARE
We are currently preparing a proposal to link SHARE data from the Czech Republic to administrative data. Similar SHARE data links already exist in Germany, Denmark and Finland.
SHARE-RV: Linking German SHARE Survey Data with Administrative Records
SHARE-RV stands for the direct linkage of survey data of the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE) with administrative records of the German Pension Insurance (DRV).
SHARE-RV is a project within the German subsample of SHARE which started as a pilot study in 2009 and is now integrated as a standard module of the German SHARE questionnaire. Upon respondents’ consent, the German Pension Insurance provides the administrative records which can be linked to the SHARE interviews of the same person.
The combination of accurate administrative data and profound information about different aspects of the respondents’ lives in SHARE-RV provide a wide range of research possibilities.
The great advantage of SHARE-RV lies in the possibility to combine administrative data of the German Pension Insurance and contextual factors of the respondents. Hence, SHARE-RV enables the investigation of connections between various aspects of respondents´ lives and their working history or their socio-economic status in later life. In addition administrative data of persons living in the same household can be identified and analysed simultaneously.
The Release 9.0.0 of the administrative data is available now. To get access to the administrative data, please follow the steps described at the project website.
REGLINK-SHAREDK: Linking SHARE Data with data from Danish national registers
REGLINK-SHAREDK is the second successful linkage project in SHARE and relates to the Danish subsample of SHARE. The linkage in Denmark was first completed in February 2017 by establishing the project as a national research infrastructure and will be consecutively updated when new waves of SHARE are released.
For the purpose of the linkage, a consortium has been established. At present, the consortium consists of University of Southern Denmark, Aarhus University, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen Business School, Aalborg University and Roskilde University.
The current version of REGLINK-SHAREDK is based on SHARE Release 9-0-0. This includes survey data of Danish SHARE respondents of waves 1-9 linked with health, labour market and demographic registers. Those respondents who gave their consent for linkage in Wave 8 are included. For the future, it is planned to provide further updates to the REGLINK-SHAREDK database, and at the same occasions update the register variable content. This will be done jointly with the release of SHARE Wave 10 data.
Survey participants were provided with information about the linkage project and asked for their written consent to linkage in accordance with the Danish Act on Processing of Personal Data. The linkage of Danish SHARE data with administrative records of the same person is carried out via a central personal identification number.
The database provides researchers from Danish research institutions with the ability to analyse employment behaviour, health conditions, ageing processes etc. and thereby provide evidenced based solutions to many of the societal challenges, which Denmark and many other countries in Europe are facing.
More information can be found at the Accompanying Datasets website of SHARE-ERIC.
REGLINK-SHAREFI: Linkage of Finnish SHARE data with administrative data
The REGLINK-SHAREFI project provides Finnish SHARE survey data linked to administrative data from Statistics Finland, Finnish Center for Pensions and Kela. The current version of REGLINK-SHAREFI includes all existing Finnish SHARE data based on SHARE Release 9-0-0 and the SHARE Corona Survey 1 & 2. Researchers can apply for administrative data separately. An update of REGLINK-SHAREFI is planned for future waves.
More information can be found at the Accompanying Datasets website of SHARE-ERIC.